CLASS A ovens are ovens for processing applications that involve solvents and vapors that are harmful to workers.
Grieve Model NBS Bench Oven(see below)
OSHA requires ovens processing flammable solvents or vapors to conform to the National Fire Protection Association Standard 86 (1999). NFPA 86 defines ovens for these applications as Class A ovens. In order to keep flammable vapor concentration at safe levels, Class A ovens include specific items of additional equipment to provide safety ventilation. This additional equipment is sized based on the volume of solvent being evaporated and the maximum operating temperature.
Safety ventilation also depends on the processing method. In batch processes, where all parts heat up at the same time, the flammable vapor concentration in not constant. As the work temperature rises the vapor concentration also rises to a peak value and then tapers off. This requires greater safety ventilation than in continuous processing where parts are heated sequentially and the vapor concentration remains constant.
|
Direct - fired gas ovens include Class A equipment to remove products of combustion. Combustion venting is sized at 183 standard cubic feet per minute of exhaust per 1,000,000 BTU/HR of burner rating. Depending on the amount of flammable solvent processed, a larger powered forced exhauster may be required to handle both combustion venting and safety ventilation.
SIZING SAFETY VENTILATION AND HEAT LOSS
Safety ventilation exhaust provides a supply of fresh air to ensure that the flammable vapor concentration in the oven remains below the Lower Flammable Limit (LFL) at all times. When more than one flammable solvent is present, safety ventilation is based on the solvent requiring the greatest amount of ventilation
Direct-fired gas heated ovens require combustion venting which must be added to the safety ventilation exhaust rate.
Combustible solids or substrates do not require safety ventilation unless flammable constituents are released when these materials are heated. Powder coating curing ovens require safety ventilation to be calculated as though 9 % of the powder weight is being evaporated as the flammable solvent Xylene.
Exhaust rates must be corrected for maximum operating temperature. As oven operating temperature increases, greater exhaust is required to compensate for the decrease in air density. Similarly, at altitudes over 1000 feet, the exhaust rate must be increased to compensate for lower air density.
• Batch Processing
For batch oven applications below 250° F, the safety ventilation exhaust rate must be sized at a rate of 440 standard cubic feet per minute for each gallon of solvent introduced into the oven in a batch. Between 250° F and 500° F, this exhaust rate must be increased by a multiplier of 1.4. Above 500° F, the 1.4 multiplier is not appropriate and a correction factor must be determined by tests run by the solvent manufacturer.
In addition, for solvents where the volume of air necessary to render 1 gallon of solvent barely explosive exceeds 2640 standard cubic feet, the exhaust rate must be increased. The increase is made by multiplying by a factor created by taking the volume of air necessary to render 1 gallon of solvent barley explosive and dividing it by 2640 standard cubic feet.
Safety ventilation and heat loss for a batch process can be estimated using the chart below. This chart shows the exhaust rate and heat loss for 0.1 gallon of solvent. The data is based on a solvent with LFL of 2640 standard cubic feet and on an installation located below 1000 feet in altitude.
• Continuous Processing
For continuous processing ovens, the safety ventilation exhaust rate must be sized to keep the concentration of solvent in the oven atmosphere below 25% of the Lower Flammable Limit (LFL) after the LFL has been corrected for operating temperature.
The specific gravity and vapor density of the solvent are used to determine the gallons of vapor created by 1 gallon of evaporated solvent. Combining this information with the Lower Flammable Limit determines the air volume rendered barely explosive when 1 gallon of solvent is evaporated. This is multiplied by a factor of 4 to limit the vapor concentration to 25% of the Lower Flammable Limit.
The safety ventilation exhaust rate is obtained by multiplying this volume by the number of gallons of solvent evaporated per minute.
Safety ventilation and heat loss for a continuous process can be estimated using the chart below. This chart shows the exhaust rate and heat loss for 0.1 gallon of Xylene. Xylene has specific gravity of 0.88 (Water = 1) and vapor density of 3.7 (Air = 1). The Lower Flammable Limit by volume is 0.9%. The amount of air rendered barely explosive per gallon evaporated is 2899 standard cubic feet. The calculated exhaust required per gallon of Xylene evaporated in continuous processing is 193 standard cubic feet per minute.
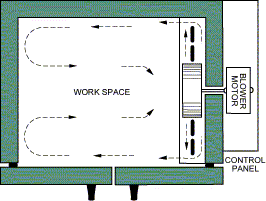
GRIEVE MODEL NBS Class A Bench Oven (Picture Above)
Model NBS-400 meets the requirements of OSHA and National Fire Protection Association Standard 86 for Class A ovens. Not for use in hazardous locations as defined in the National Electric Code.
These rugged bench ovens are designed for a wide variety of industrial heat processing applications including those where flammable solvents or vapors will be present in the oven.
Fan forced recirculation of heated air throughout 7 cubic foot work space at temperatures to 400°F. Includes two (2) removable nickel plated wire shelves easily adjustable on 2" centers. Holds a maximum of seven (7) shelves. Includes safety equipment required when flammable solvents or vapors are present in an oven.
STANDARD FEATURES
— Recirculating blower
— 304 stainless steel interior — Incoloy sheathed tubular heating elements — Silicone rubber door gasket — Analog, thermocouple actuated, temperature controller — Adjustable, thermocouple actuated, manual reset excess temperature interlock — On-off switch — Red pilot light indicates heater operation — Sturdy steel construction — Brushed stainless steel exterior — 6 lb/cf density industrial rockwool insulation — Built-in baffles prevent radiant heat — Fully factory tested — 1 year limited warranty
Completely wired control panel assembled on the oven enclosing the temperature controller, manual reset excess temperature interlock, pilot light to indicate when heaters are energized and on-off switch. Includes additional safety equipment required by OSHA and NFPA 86 for Class A ovens. Will handle a maximum of 3 ounces (0.024 gallons) of flammable solvents or vapors per batch at a maximum temperature of 400°F.
• Manual Reset Excess Temperature Interlock
Turns off heat if oven exceeds 400°F.
• Back-Up Heating Element Relay
Turns off oven heat on excess temperature controller actuation in the
event of failure of the primary heating element relay
• 35 CFM Separately Powered Forced Exhauster
Provides safety ventilation. Exhaust outlet 4" diameter.
• Exhauster Air Flow Safety Switch
Turns off oven heat if exhauster fails
• Recirculating Blower Air Flow Safety Switch
Turns off oven heat if recirculating blower fails
• Purge Timer
Provides time delay to allow exhauster to pull four oven volumes of
air through the oven prior to turning oven heat on
216-360-9800 / 614-885-3933 / 513-528-5680
grieve@anderson-bolds.com
Cleveland - Cincinnati - Columbus
Ohio - West Virginia - Kentucky
|

No comments:
Post a Comment